Selecting the right 3D printing process depends on many factors, including the purpose of the part, its size and its material. 3ERP can help you decide on the appropriate 3D printing technology for your project.
3D printing services we offer:
1.FUSED DEPOSITION MODELING (FDM)
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is the most widely used additive manufacturing process for desktop 3D printers. The process involves extruding a melted plastic from a computer-controlled nozzle, building a part layer by layer.
FDM 3D printers use a spool of filament as raw material. This filament is directed into the print head, where it is melted and deposited onto the incomplete part. In accordance with computer instructions, the print head moves along 3 axes in order to deposit material in the right place.
Because the material cools after it is deposited, further layers of material can be deposited on top of the existing layers, allowing for the creation of 3D shapes.
FDM is also known as Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF).
Advantages
- Most affordable 3D printing process for plastic parts
- Material options
- Widely available
Disadvantages
- Comparatively low resolution
- Produces visible layer lines
Typical accuracy
- ± 0.5% (desktop)
- ± 0.15% (industrial)
Typical layer height
- 50-400 microns
FDM Materials
PLA: The most widely used FDM material, PLA (Polylactic Acid) is affordable, stiff and strong. It also comes in many colors and blends.
ABS: Another common FDM material, ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is also resistant to high temperatures.
PETG: PETG (Polyethylene terephthalate) has high impact resistance and good thermal characteristics. It is also food safe.
Nylon: Tough and flexible, nylon is strong and resistant to wear and chemicals. It is, however, vulnerable to humidity.
TPE/TPU: A blend of plastic and rubber, these thermoplastic filaments produce highly flexible parts.
PC: PC (Polycarbonate) filaments produce extremely strong parts that are resistant to heat and impact.
2.STEREOLITHOGRAPHY (SLA)

Stereolithography (SLA) is an additive manufacturing process that works in a different way to FDM. In SLA 3D printing, a 3D object is created with a laser, which is directed at areas of photosensitive liquid resin. The laser causes areas of the resin to harden, forming a solid part.
The SLA process uses a moving platform in a tank of liquid resin. The platform moves up or down after each layer is fully cured, which is different to FDM, in which the platform remains stationary. The SLA laser is focused using a system of mirrors.
SLA can only be used with photosensitive polymers, but offers high accuracy and fine details. It also predates other forms of additive manufacturing, having been invented back in the 1980s.
Advantages
- High resolution
- No visible layer lines; smooth finish
- Option of clear materials
Disadvantages
- Printers more expensive than FDM
- Weak parts will degrade with sunlight
- Extensive post-processing required
Typical accuracy
- ± 0.5% (desktop)
- ± 0.15% (industrial)
Typical layer height
- 25-100 microns
Stereolithography Materials
Resin 8119: A common SLA material with a temperature resistance of up to 65°C.
Resin 8118H: A nylon-like resin with exceptionally high tenacity.
Resin 8228: An ABS-like resin resistant to impact and temperatures up to 70°C.
Resin 8338: The most temperature-resistant of our resins, able to withstand temperatures up to 120°C.
3.SELECTIVE LASER SINTERING (SLS)
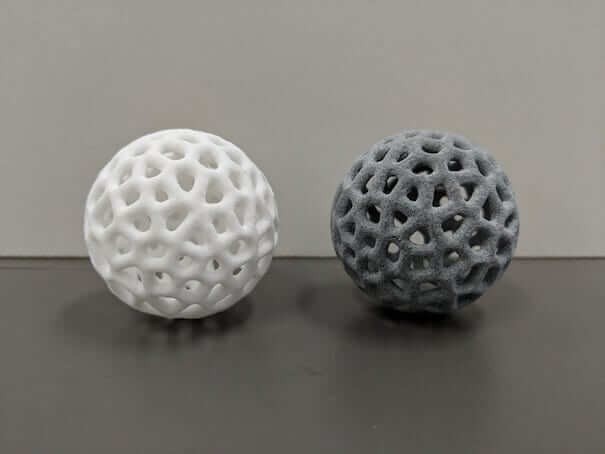

Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is a powder bed additive manufacturing process used to make parts from thermoplastic polymer powders. It is commonly used for functional parts, since SLS printed components have good mechanical properties.
An SLS 3D printer works by sintering areas of powder with a laser. During the process, a thin layer of powder is distributed evenly across the build platform, after which the laser sinters selected areas of the 2D layer. When the layer is complete, the platform is lowered, more powder added, and the laser sinters the next layer.
When all layers are complete, the part is left to cool. Unused powder is kept to be used again, and the part is cleaned to remove excess material.
Advantages
- Parts have consistent mechanical properties
- No support structures
Disadvantages
- Porosity
- Rough surface finish
Typical accuracy
- ± 0.3%
Typical layer height
- 100-120 microns
SLS Materials
Nylon PA12: An SLS material that offers mechanical strength and thermal and chemical resistance, as well as long-term stability.
Alumide: Aluminium-filled nylon provides high stiffness and a metallic appearance.
TPU: A highly elastic material with high tear and abrasion resistance, as well as satisfactory thermal resistance.
4.SELECTIVE LASER MELTING (SLM)
Selective Laser Melting (SLM) is a metal additive manufacturing process used to create functional, end-use products. SLM printers use a laser to melt particles of metal powder, fusing them together to form a 3D object.
An SLM 3D printer uses a gas-filled chamber containing the metal powder. The laser passes over the desired sections of the powder, causing the particles to melt and bond. When a layer is complete, the build platform moves down to allow the laser to pass over the next layer.
The SLM process can be used to create strong metal parts with highly complex shapes, providing engineers with new levels of design freedom.
Advantages
- Strong and hard parts
- Complex shapes
Disadvantages
- Limited build size
- High cost
Typical accuracy
- ± 0.1mm
Typical layer height
- 20-50 microns
SLM Materials
Titanium: Titanium alloys (6Al-4V and 6Al-4V ELI) can withstand high temperatures, offer a high strength-to-weight ratio and are resistant to corrosion. Can be heat treated for superior strength.
Aluminum: Aluminum alloys (AlSi12 and AlSi10Mg) provide strength and hardness, and work well with complex shapes or parts with thin walls.
Stainless Steel: Stainless steels are resistant to wear, corrosion and abrasion.
Cobalt: Cobalt-chrome alloys offer high strength, hardness and resistance to high temperatures.
Nickel: Nickel alloys are resistant to heat, corrosion and oxidation, and create parts with strength in high-temperature environments.
Precious Metals: Metals like gold, silver and platinum are ductile and provide a desirable appearance.


